Contents
0%Flows, node-based AI interfaces, are the backbone of AI Flow Chat. They represent the logical sequence of operations that your app will perform, from receiving input to generating output. Think of flows as visual programs that you can create by connecting different nodes together.
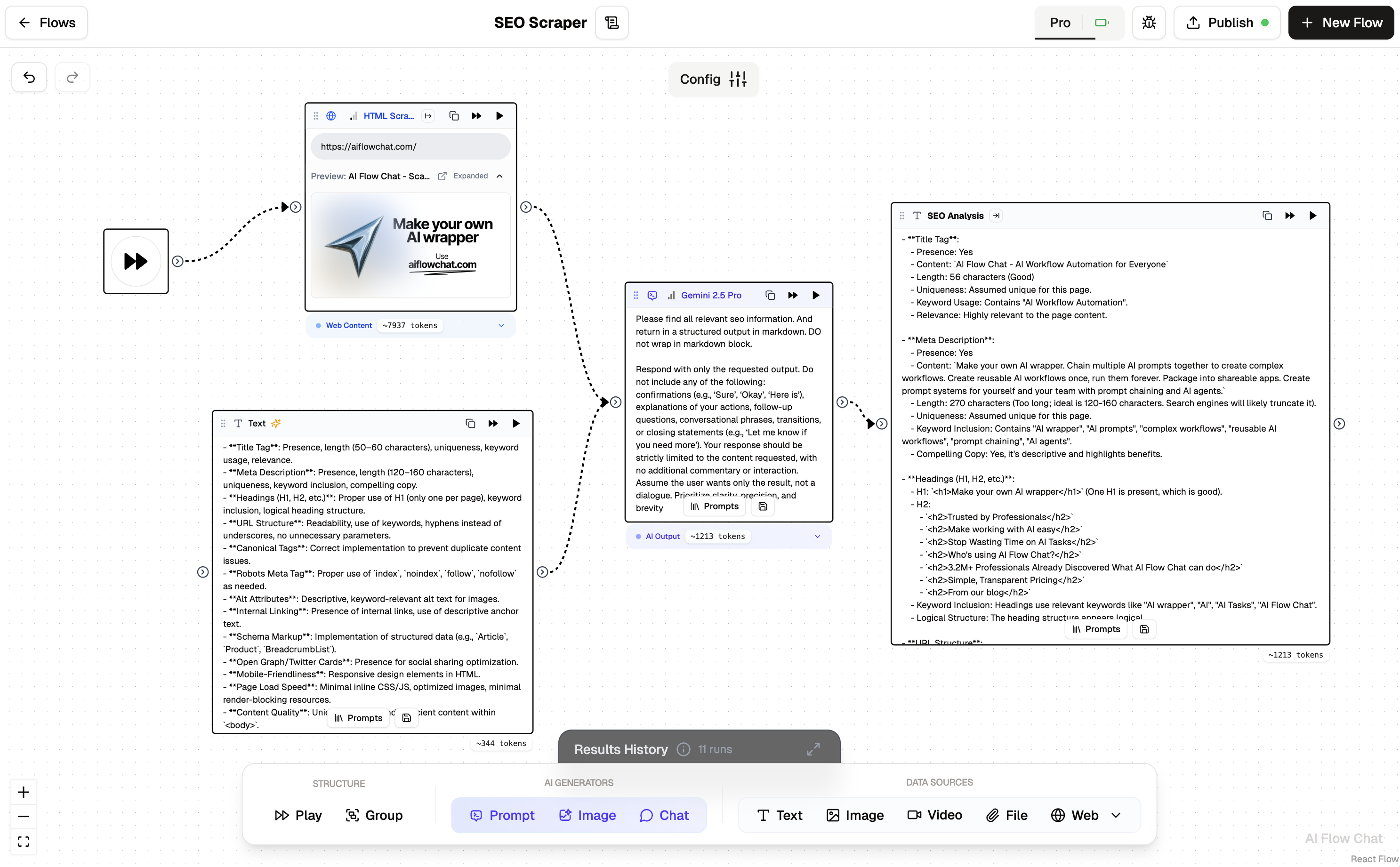
Flows Overview
Flow Components
Nodes
Nodes are the building blocks of your flows. Each node performs a specific function.
We have three node categories:
- AI Generators: Nodes that generate AI content (e.g. Text, Image, etc.)
- Data Sources: Nodes that act as a source of data (e.g. Text, Web, File, etc.)
- Structure: Meta nodes that help you structure your flow (e.g. Play, Groups, etc.)
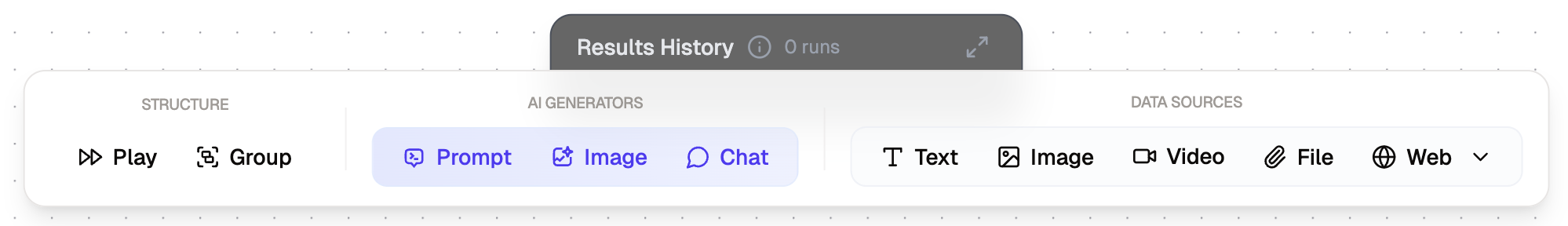
Nodes Overview
Nodes have inputs and outputs that you can connect to create complex workflows.
Nodes can be run by clicking the run button on the node. Running a node will generate the node's output data. Running a node will typically consume user credits. The number of credits consumed depends on the node.
E.g. a prompt node will generate text, an image generator node will generate an image, a web node will fetch content from a website, etc.
Connections
Connections link nodes together, allowing data to flow from one node to another.
The output of one node becomes the input for the next node in the sequence.
How you connect the nodes will determine the order of the data flow. It's always left to right.
So the right node will use the data from the left node.
You can connect one output to multiple inputs.
You can also connect multiple outputs to one input.
Text and Image nodes
Text and Image nodes are special nodes that can be used to:
- act as input to other nodes.
- act as output to see the output from your flow.
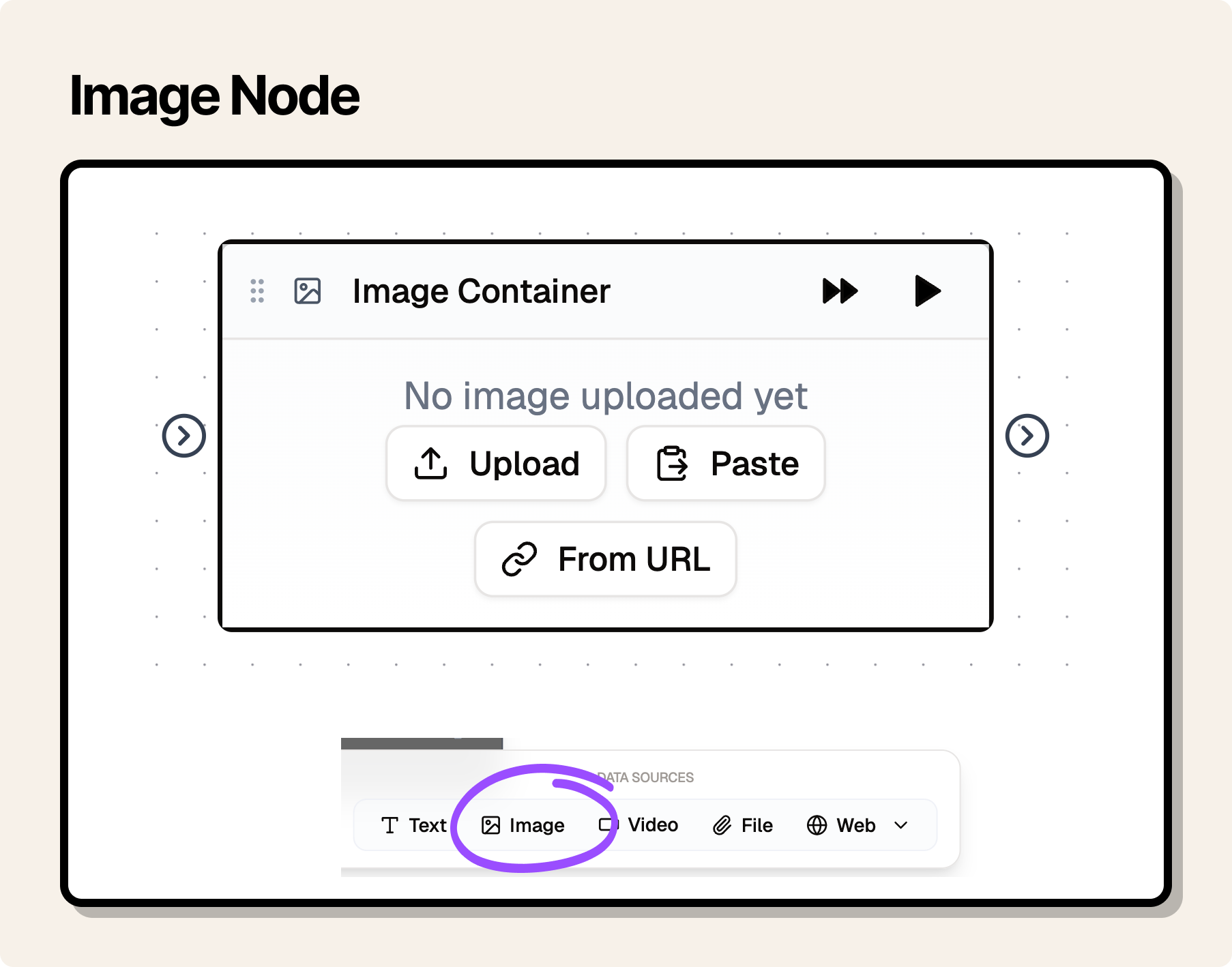
Image Node
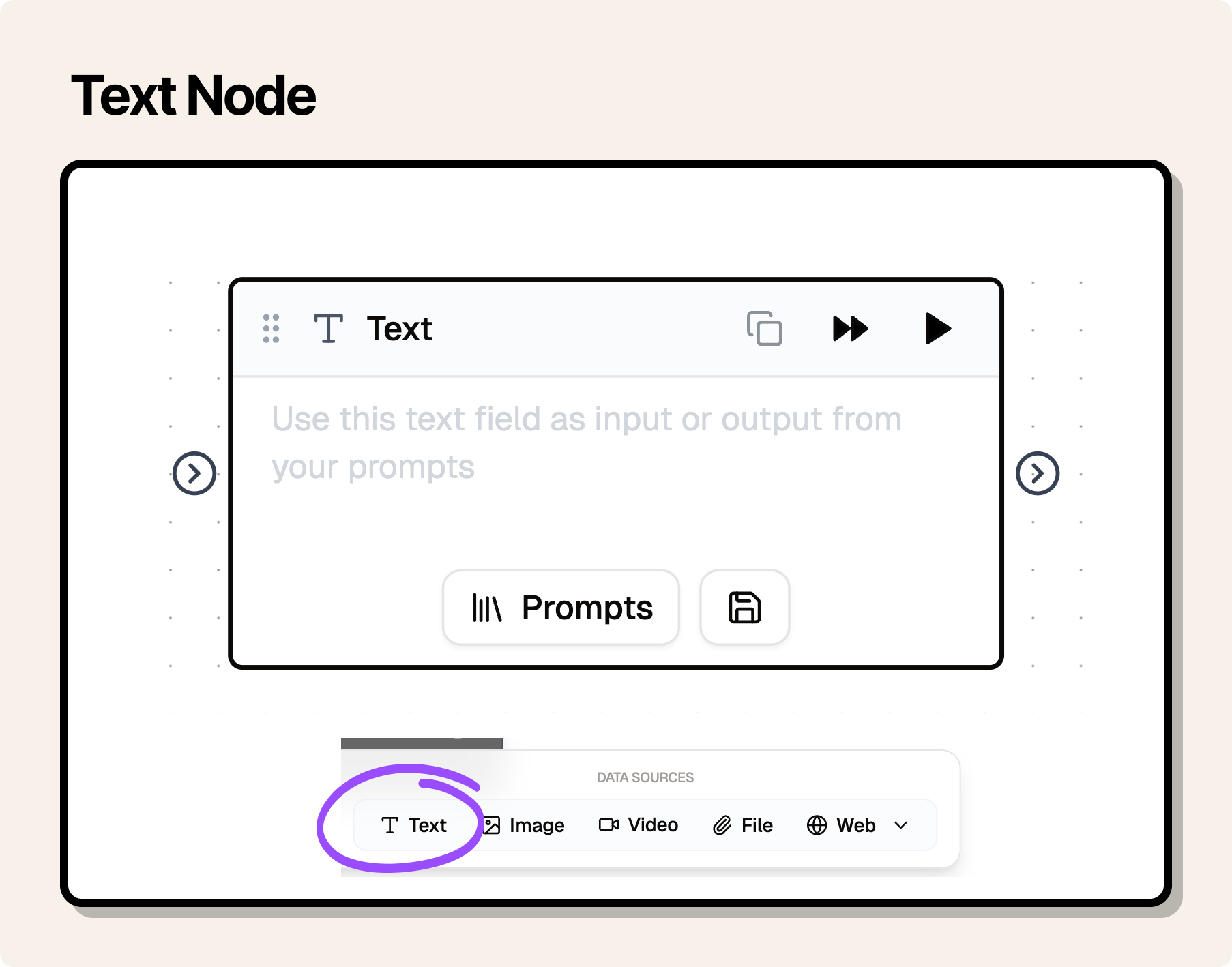
Text Node
The 3 types of Node Data
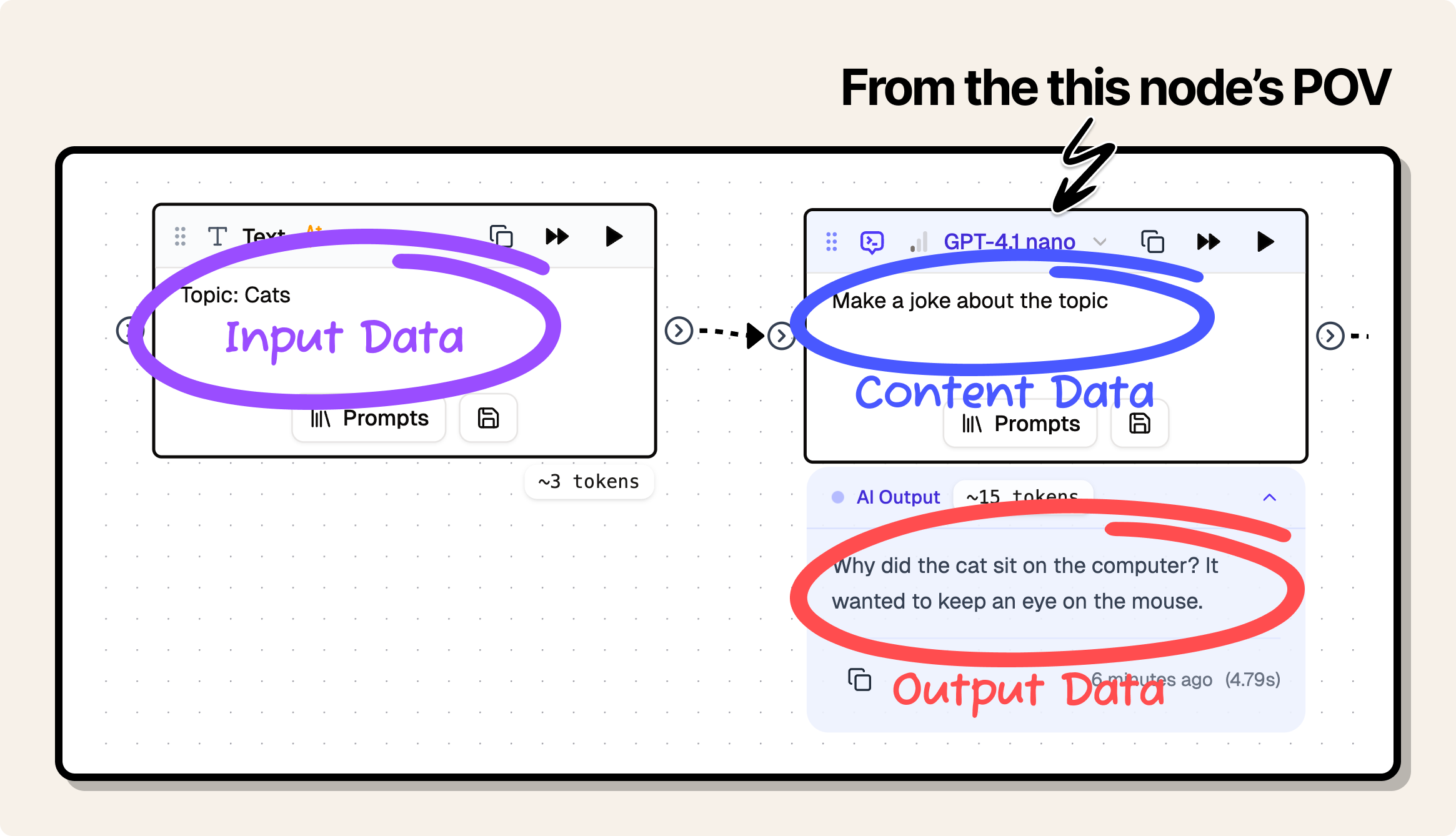
Input Content Output
Nodes have three types of data:
-
Content:
- This is the settings and data of the node that the user has set directly in the node.
- Example: the prompt of a Prompt node, the URL of a Web node, the file of a File node, etc.
-
Input: Data that is passed to the node.
- This is the data that is passed to the node from the previous node(s).
- Example: An image from an image generator node, or the text from a prompt node.
-
Output: Data that is passed from the node.
- This is the data that is passed to the next node(s).
- Example: The image from an image generator node, or the text from a prompt node.
Output data needs to be generated by having run a node at least once.
After a node has been run, the output data is stored in the node.
You can see if a node has output data by checking if an output block appears underneath the node.
Clicking the output block will show what the output data is.
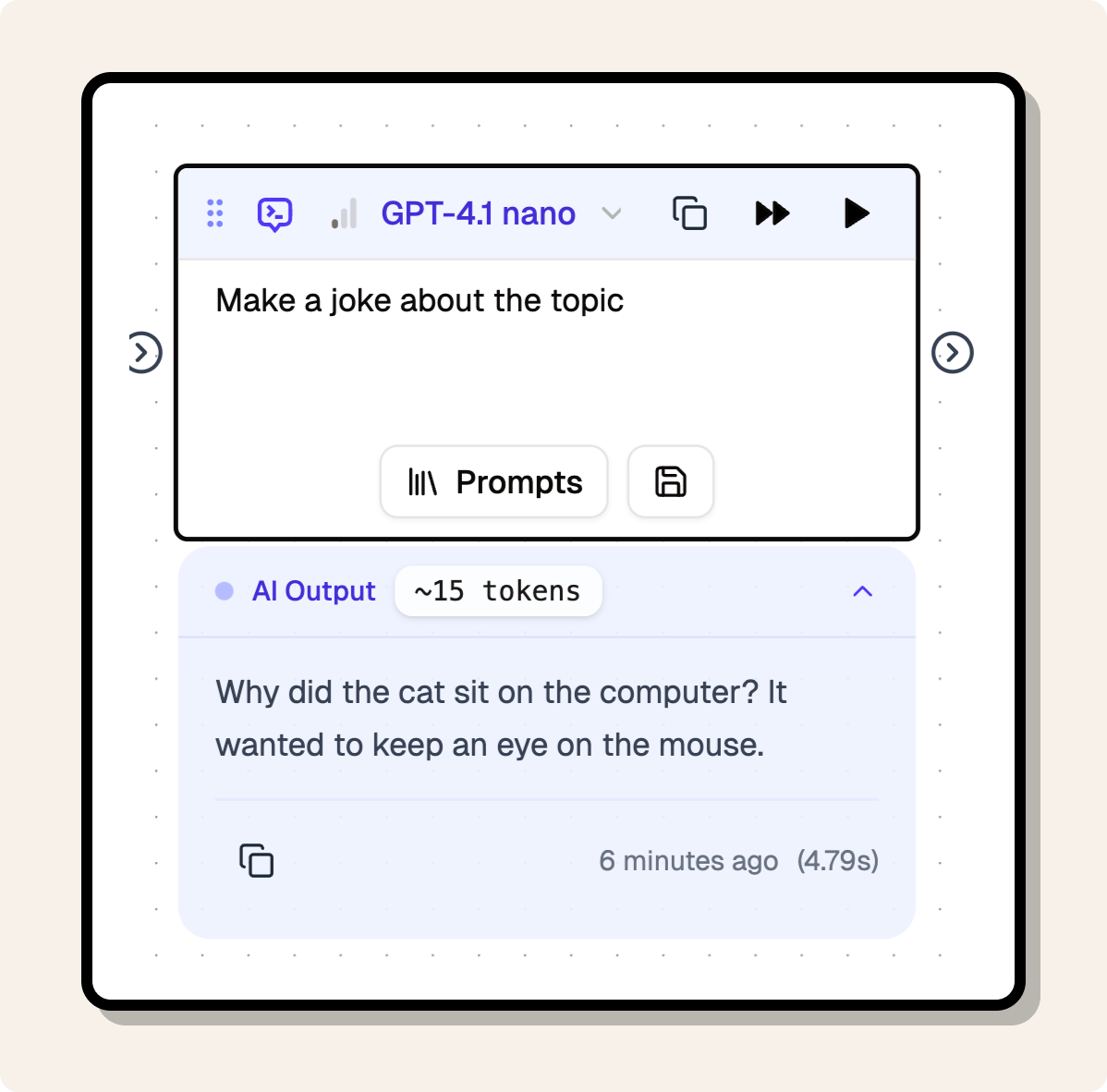
Node Output Modal
Output data needs to be generated by running the node. However, there are three nodes that do not need to be run to generate output data:
- Play: The play node is a special node that is used to play a flow. It does not generate any output data.
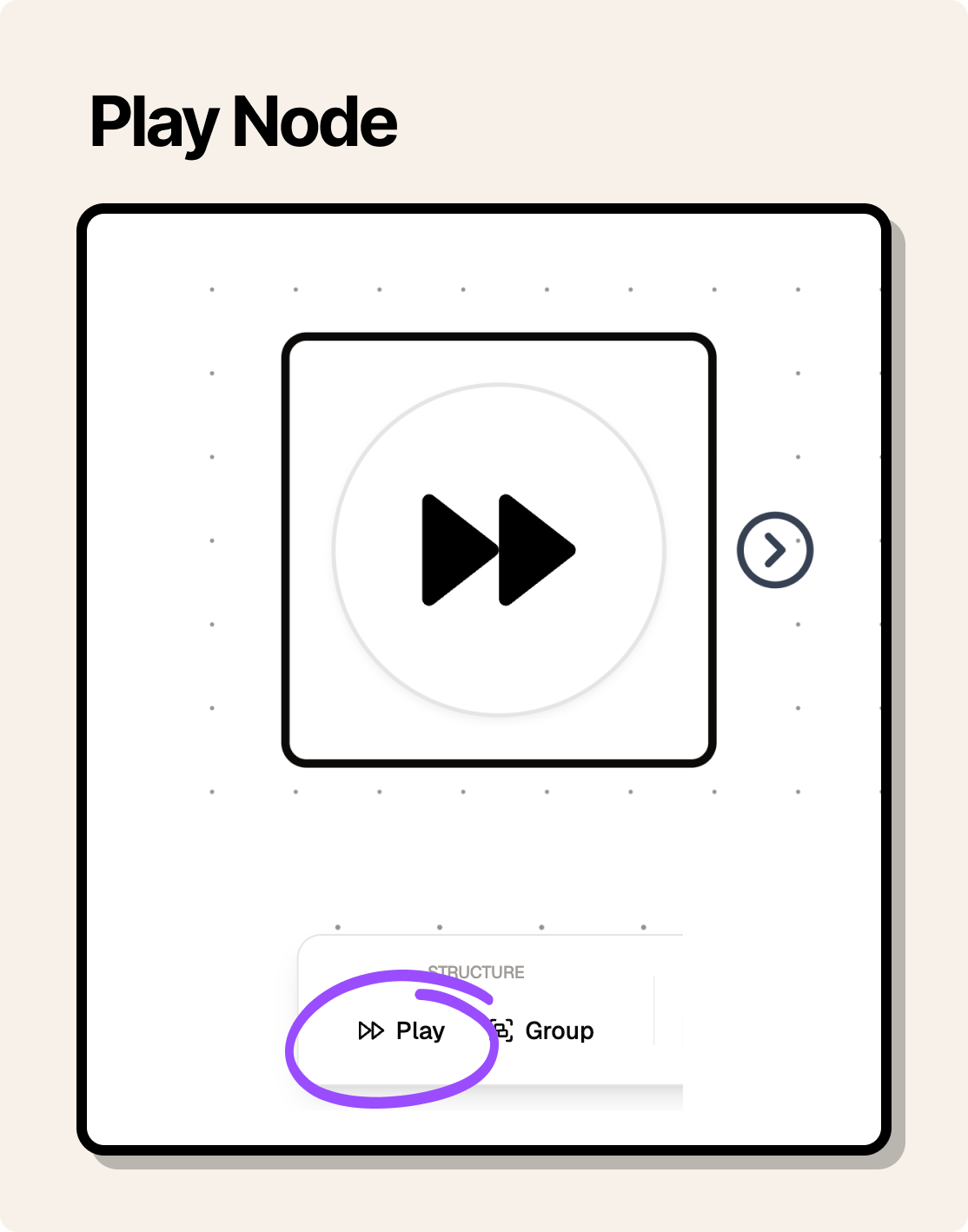
Play Node
- Text: The intenal data, i.e. the text of the node written by the user is automatically used as output data.

Text Node
- Image: The intenal data, i.e. the image of the node uploaded by the user is automatically used as output data.

Image Node
Flows - A connection of nodes
A flow is a connection of two or more nodes.
Running a flow will run all nodes connected to each other from the starting point where you click the run button.
A running flow can be stopped by clicking the stop button on the play node or any node in the flow.
Getting Started
Create a new flow
To create a new flow, click the "New Flow" button in the top right corner in the Dashboard.
You'll be redirected to the flow editor and met with a default canvas setup.
From here you can remove the default nodes, or built on top of it.
You're good to go!
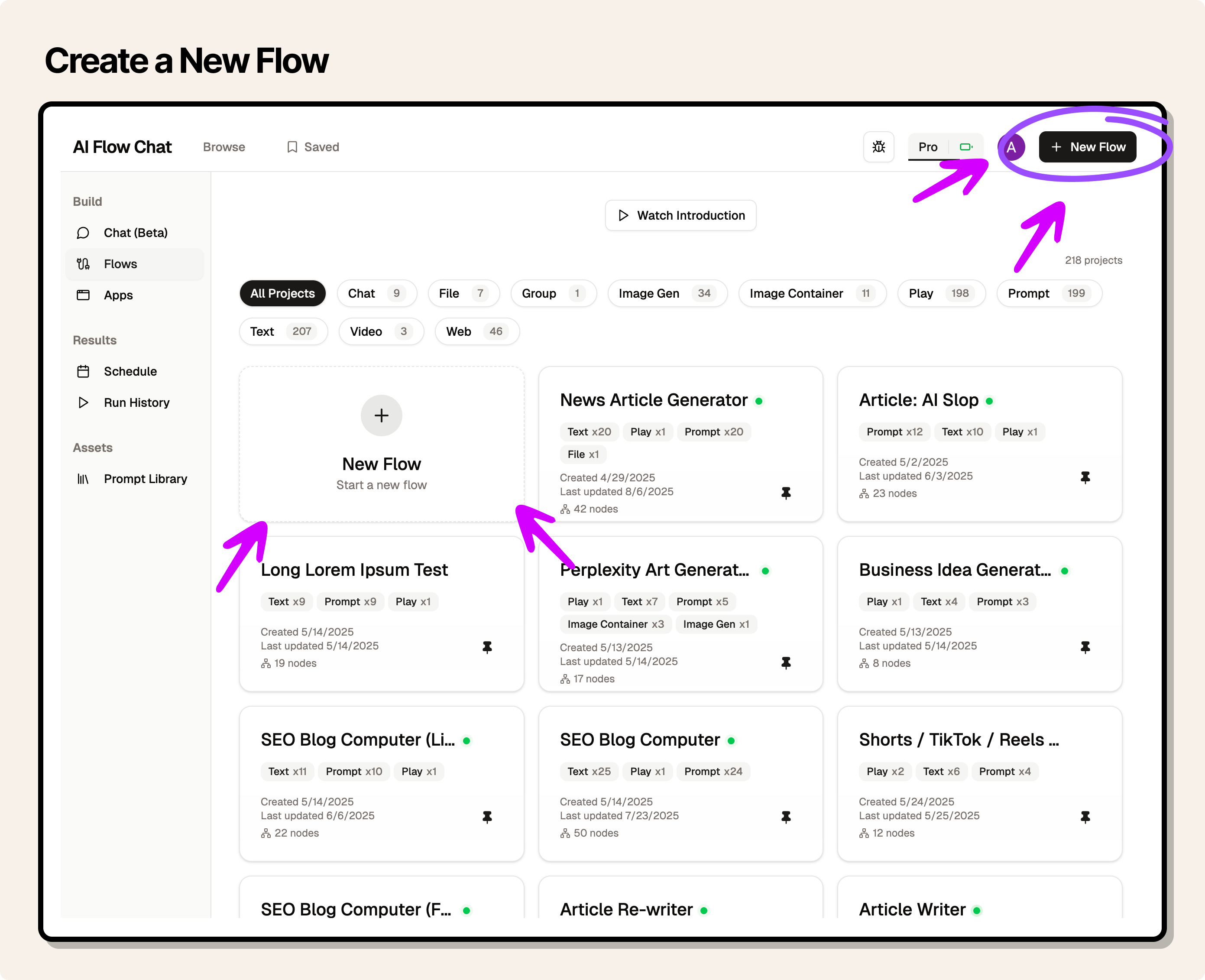
Dashboard
Add nodes
There are multiple node types available, each with its own purpose.
On the bottom of the canvas you can see the node palette. You can add a node by clicking on it or dragging it from the node palette to the canvas.
Some nodes will be automatically generated when you paste content or drag files to the canvas.
For example when you paste a URL, a Web node will be automatically generated. Dropping a file will generate a File node. Dropping an image will generate an Image node.
Connect nodes
On each node, you'll find input and output handles. You can connect a node to another node by dragging the output handle of one node to the input handle of another node.
The flow of data follows these connections from left to right. Left handle is always the input handle and right handle is always the output handle.
Run a flow
There are two ways to run a flow:
- Click on the double play button on the top left of the canvas.
- Click on the run button on the play node.
You can also run the flow from a specific node ignoring all previous nodes before it. This is useful if you have made a change on a specific node and you want to rerun the flow from that node.
Run Buttons
Flow Patterns
Linear Flows
Simple sequence of nodes where data flows from start to finish in a straight line. Good for basic processing tasks.
Parallel Flows
Save time by running multiple nodes in parallel.
Chat Flows
Bring in sources and generated data into context. Ideate with a Chat that has knows what you are talking about.
Read more about Chat Flows.