More Prompts:
Best prompts for ChatGPT for coding using debugging complex algorithms
12 practical, copy-ready prompts to debug, diagnose, and fix complex algorithmic and systems bugs across languages (C/C++, Java, Python). Each entry includes a concise title, explanation, a ready-to-use prompt, a realistic example, and recommended AIs.

Stop Losing Your AI Work
Tired of rewriting the same prompts, juggling ChatGPT and Claude in multiple tabs, and watching your best AI conversations disappear forever?
AI Flow Chat lets you save winning prompts to a reusable library, test all models in one workspace, and convert great chats into automated workflows that scale.

“AI Flow Chat powers our entire content strategy. We double down on what’s working, extract viral elements, and create stuff fast.”
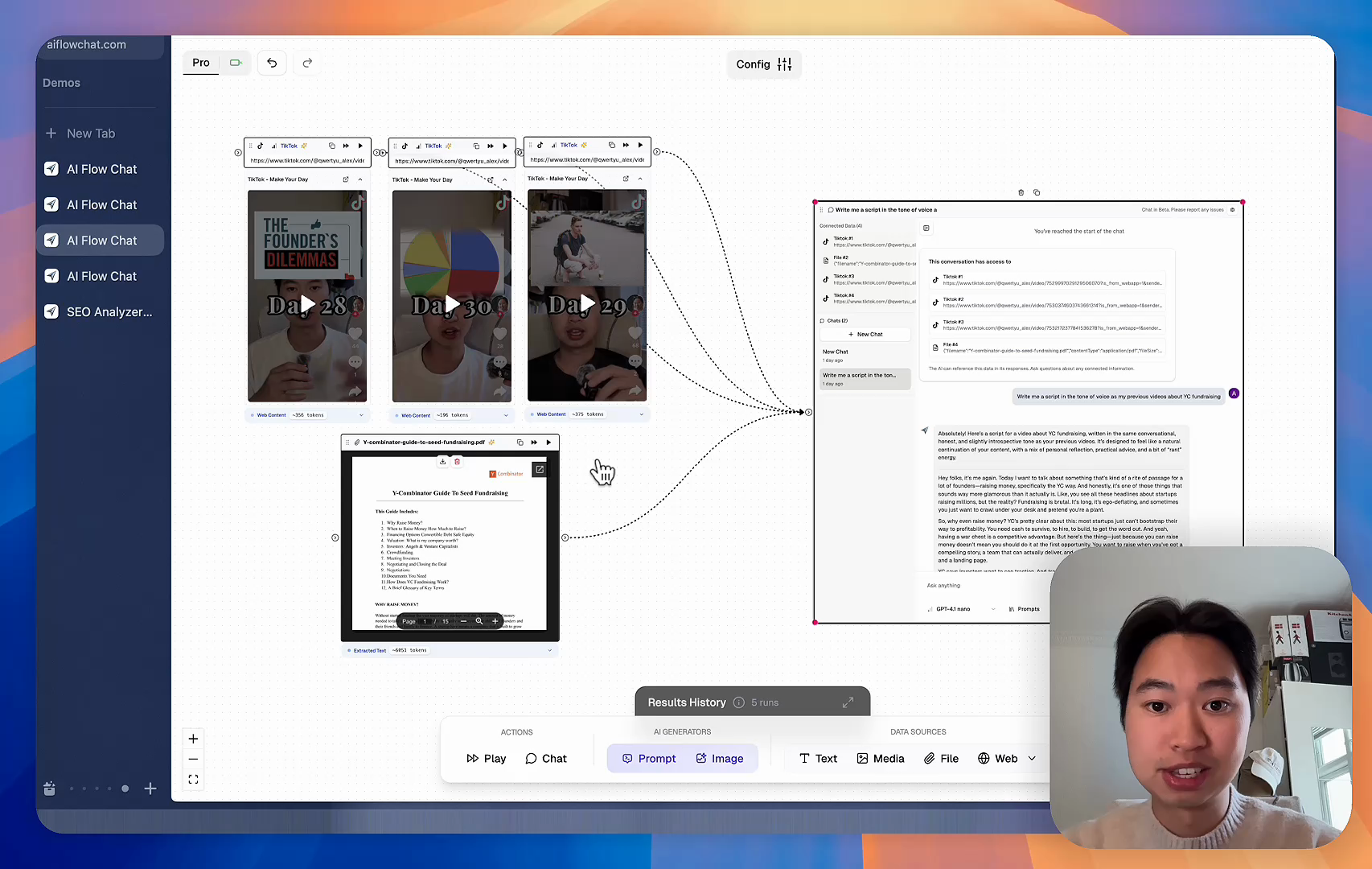
Reference Anything
Bring anything into context of AI and build content in seconds
YouTube
DOCX
TikTok
Web
Reels
Video Files
Twitter Videos
Facebook/Meta Ads
Tweets
Audio Files
Choose a plan to match your needs
Upgrade or cancel subscriptions anytime. All prices are in USD.
For normal daily use. Ideal for getting into AI automation and ideation.
- See what Basic gets you
- 11,000 credits per month
- Access to all AI models
- 5 app schedules
- Free optional onboarding call
- 1,000 extra credits for $6
No risk, cancel anytime.
For power users with high-volume needs.
- See what Pro gets you
- 33,000 credits per month
- Access to all AI models
- 10 app schedules
- Remove AI Flow Chat branding from embedded apps
- Free optional onboarding call
- 2,000 extra credits for $6
No risk, cancel anytime.
Frequently Asked Questions
Everything you need to know about AI Flow Chat. Still have questions? Contact us.
